Lower Paleolithic

3.3 m years ago- 300 000 years ago
The Lower paleolithic period marks the first use of stone tools by hominins.
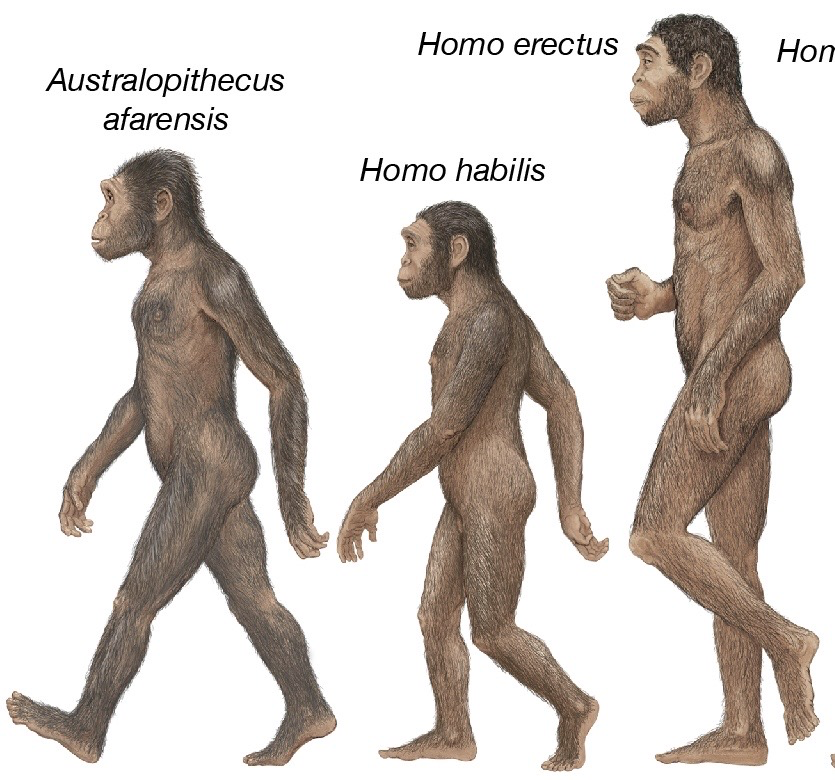
During this lower paleolithic period hominins began to evolve over 3 million years starting from Austrapolithicus to the first Homo Sapiens
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Lower Paleolithic Tools
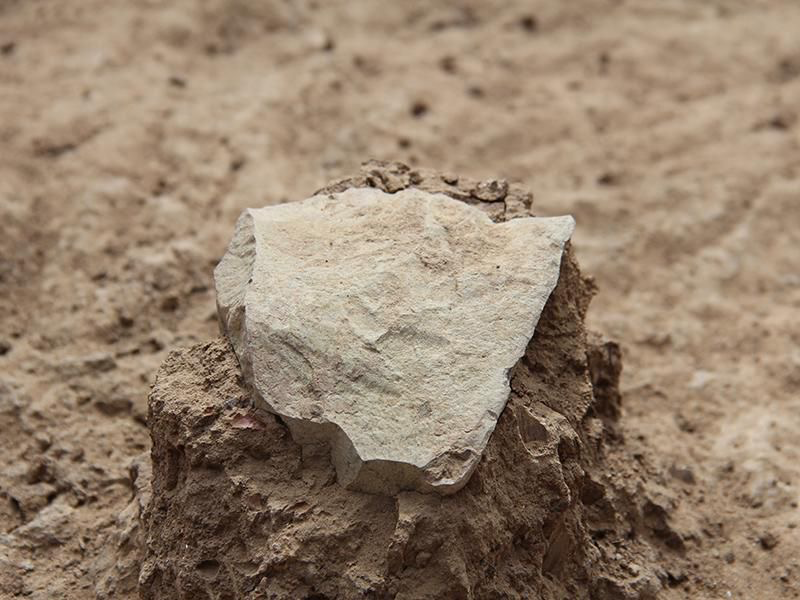


Lomekwi Stone Tools
The oldest stone tools discovered
3.3 million years old found in Kenya
The tool was most likely made and used by Australopithecus
Stones were used as choppers, scrapers and pounders
Core and chopper pieces were flaked
Flaked fragments were taken from the core pieces
Pounders were used to flake the core pieces

Oldowan Stone Tools
Made and used between 2.6m-1.7m years ago
Used across Africa, South Asia, Middle East and Europe
The tools were potentially made and used by Australopithecus
Homo habilis and homo erectus would then inherit the technology and refine it 1.7m years ago
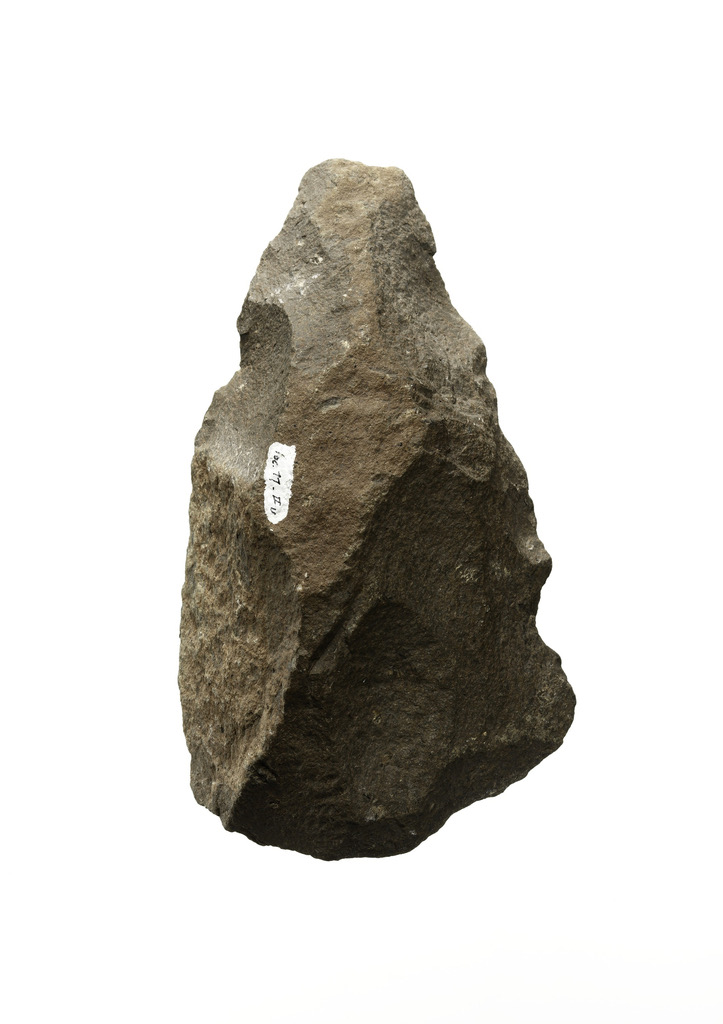

Acheulean Hand Axe
Oldest hand axe ever found
1.76m years old Found in Kenya
Made by homo erectus
Hand axes were made until around 300 000 years ago
Usually made from flint or chert
Used to butcher animals, dig for tubers, animals or water, chop wood, remove tree bark and to throw at prey
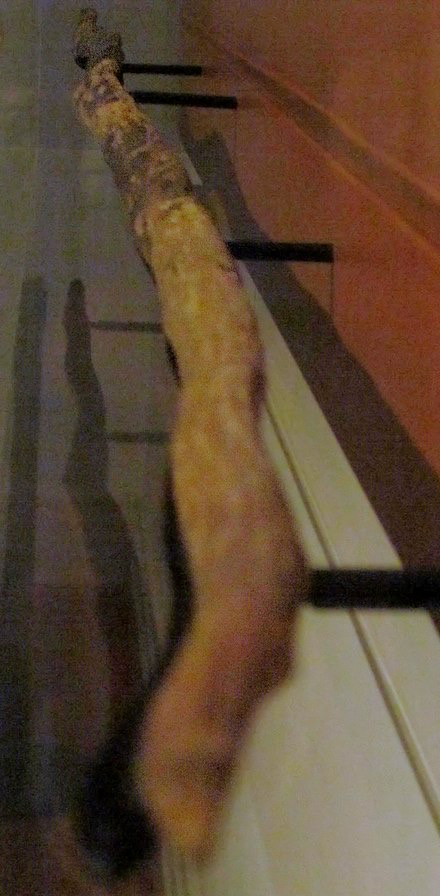


Schöningen Spears
400 000 year old wooden throwing spears
Found in Germany
Thought to belong to Homo Heidelbergensis


____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
First Stone Tool Makers
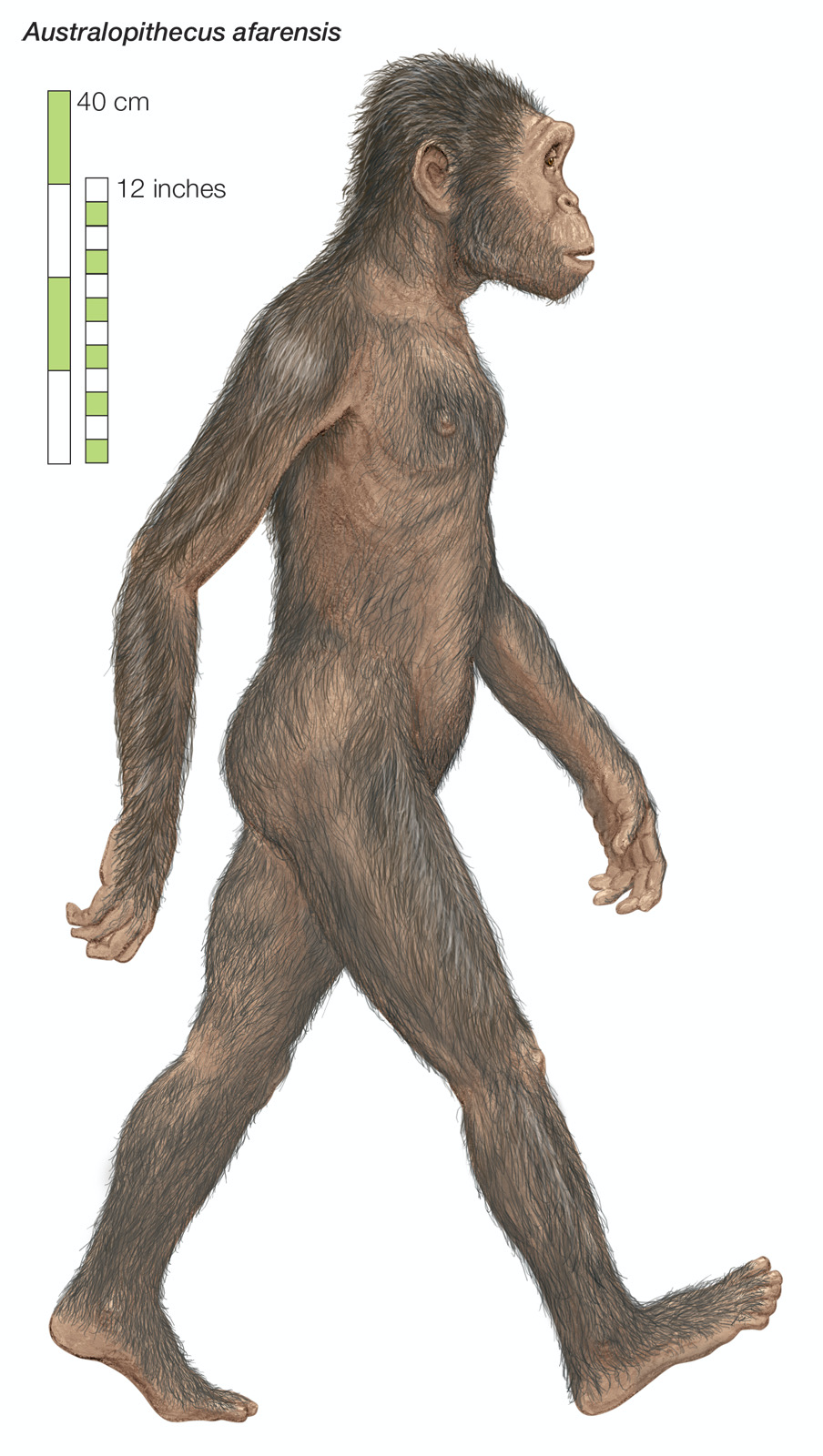
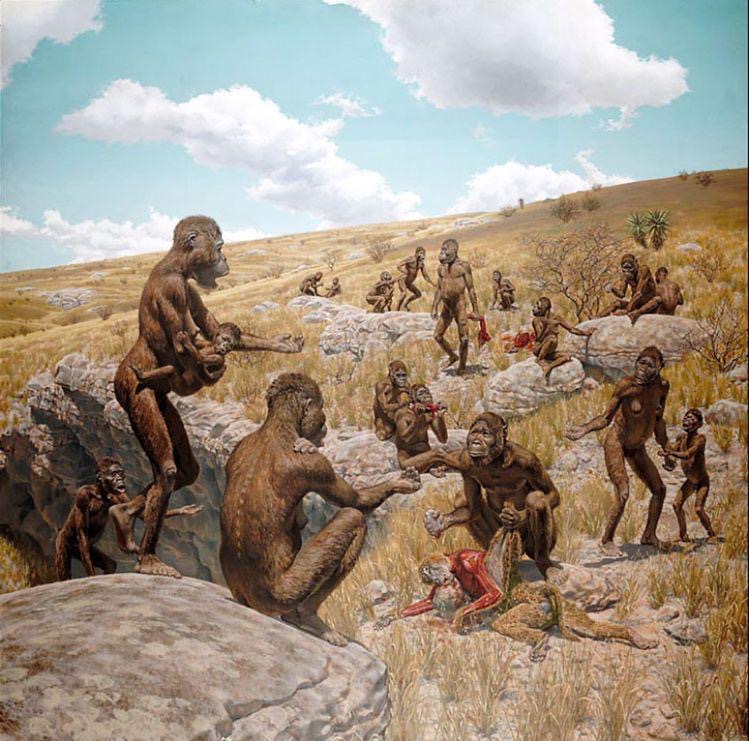
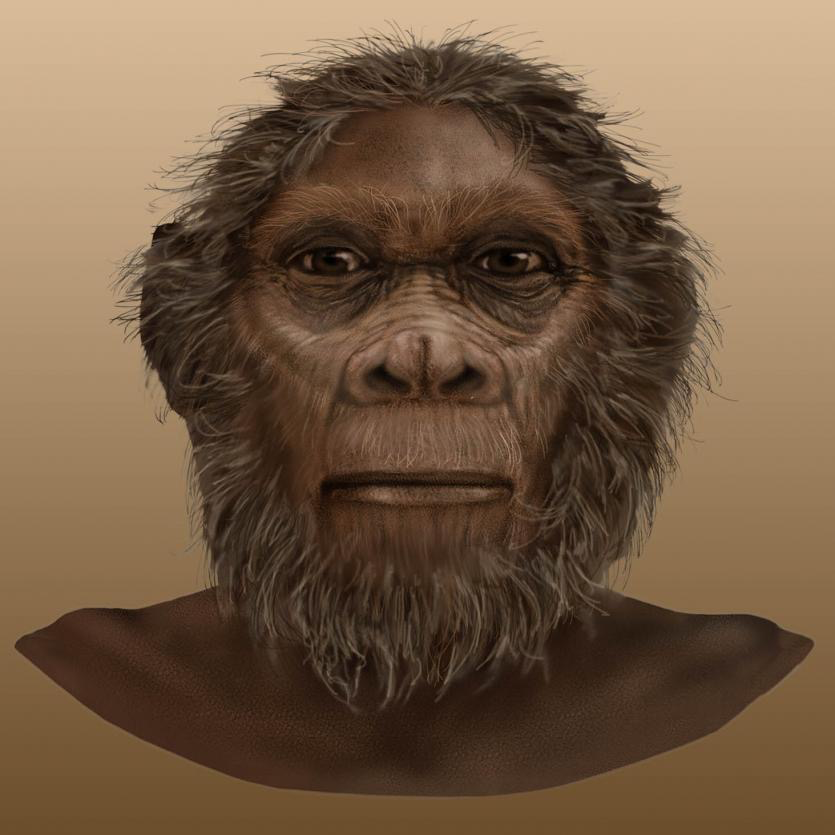
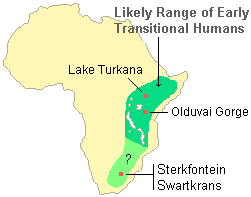
Australopithecus
Australopithecus evolved in Africa around 4.2m years ago
There are many sub species of Australopithecus
Spread through the continent of Africa
Became extinct 1.9m years ago
Scavenged for fruit, vegetables, lizards and tubers
Australopithecus afarensis and Australopithecus gharhi were the only species known to make and use stone tools

Homo Rudolfensis
Evolved from Australopithecus in Africa around 2.4m years ago
Lived during a time when stone tools were being used so it is highly likely they made and used tools
Omnivorous scavengers
Became extinct around 1.7m years ago
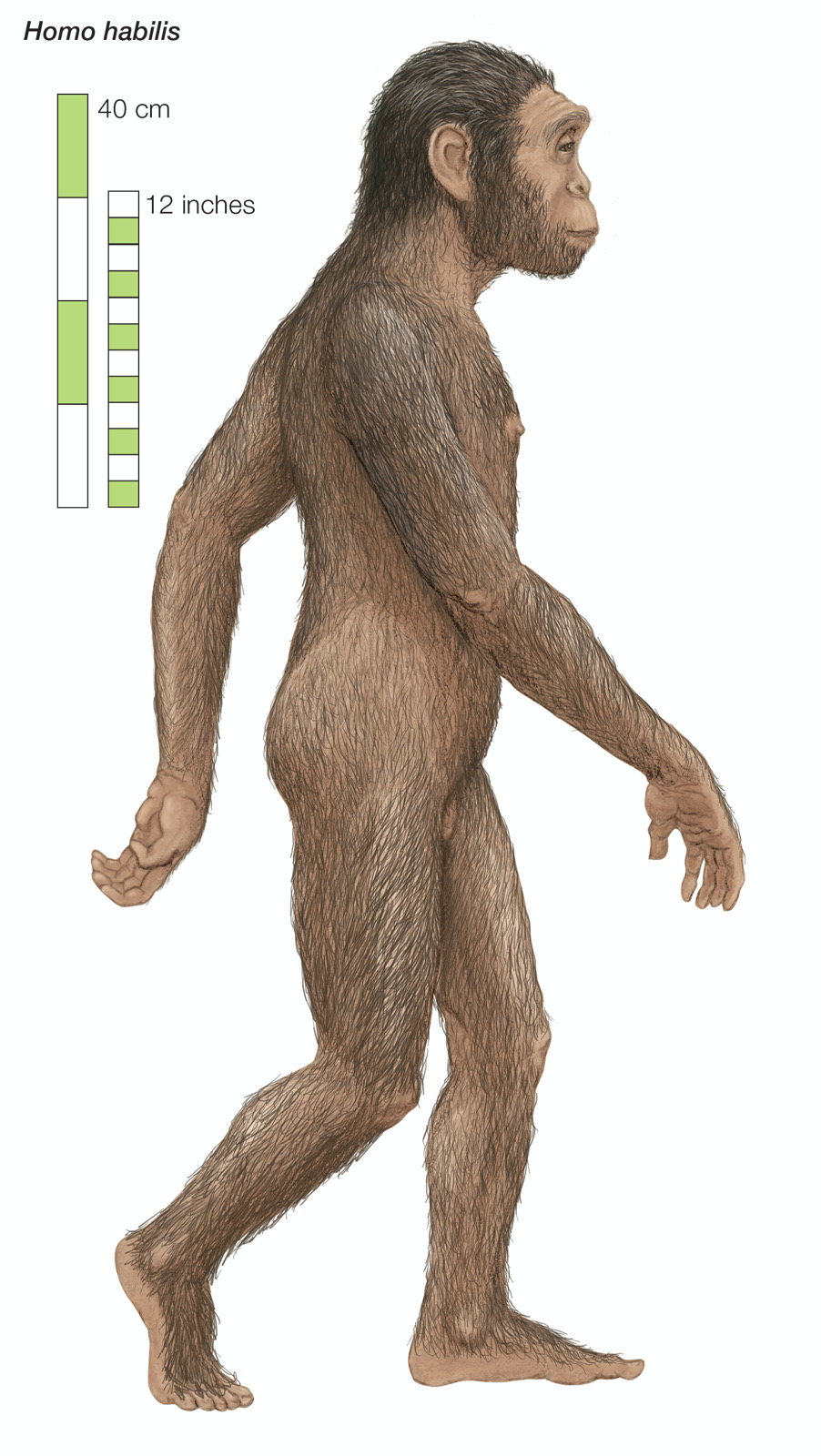


Homo Habilis
Evolved from Australopithecus around 2.3m years ago
Used oldowan tools to butcher and skin animals
Scavenged for dead animals and fruit
Used stone tools for cleaving meat off of dead animals
Were the first hominins to build shelters
Became extinct around 1.5m years ago
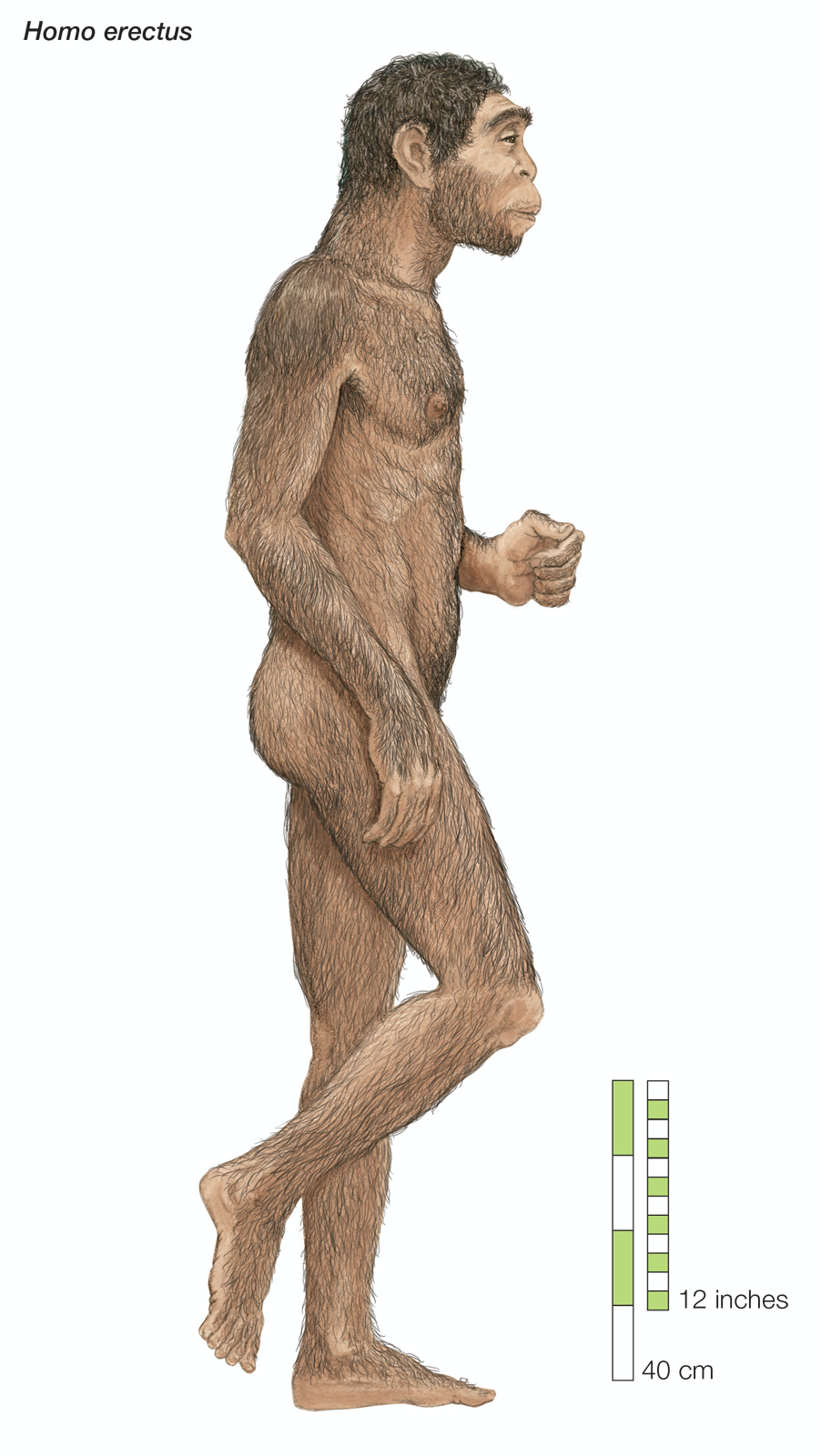

Homo Erectus
Evolved from homo habilis 2m years ago
There are many different sub species of homo erectus
Spread through the continent of Africa, West Asia, east Asia South East Asia and Europe
Became the first hunter-gatherers
First hominins to create fire and cook food
Became extinct between 50 000 to 100 000 years ago

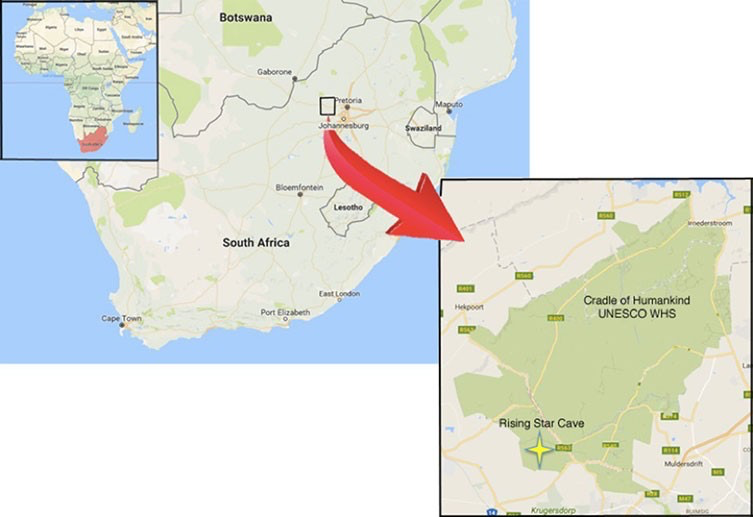
Homo Naledi
Evolved in Africa around 2m years ago
Little is known about the Homo Naledi
It is thought to have eaten grasses, sedges, grit and dirt.
Fossils have been found in caves it is unknown if they performed burials
They may have become extinct 200 000 years ago
Homo Antecessor
Evolved from Homo Erectus in Western Europe around 1.2m years ago
May have evolved from homo erectus
Used Olduwan style stone tools used for cleaving meat and breaking bone to eat the marrow
Antecessors scavenged and possibly hunted large mammals and supplemented their diet with vegetables
Became extinct 800 000 years ago

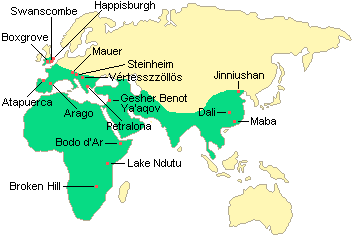
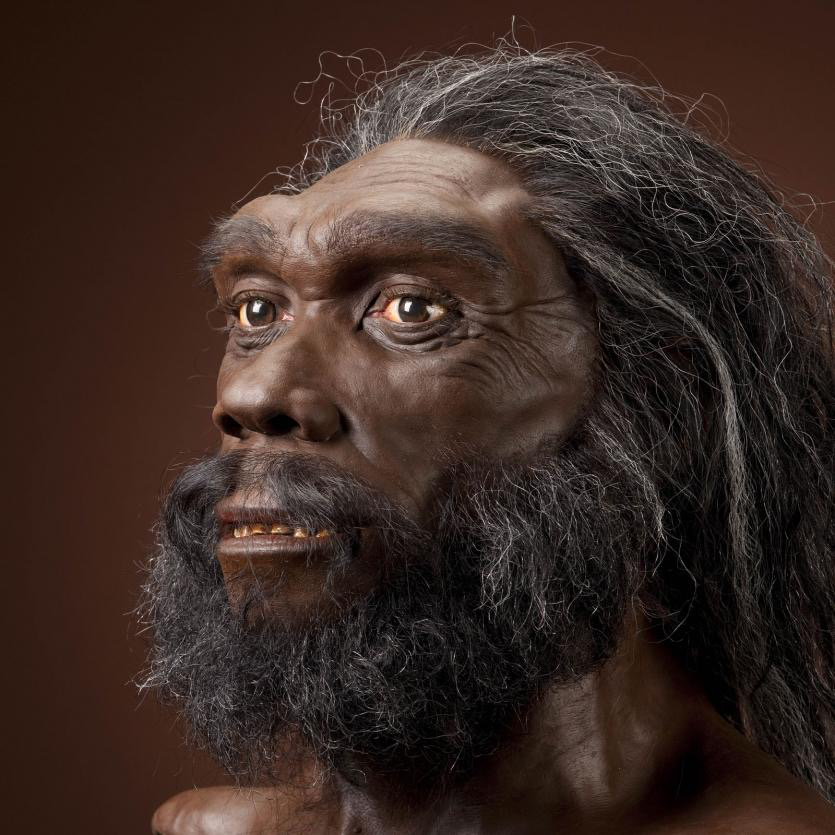
Homo Heidelbergensis
Evolved from Homo Erectus in Europe and Africa around 700 000 years ago
May be the first specifies to perform burials
Used spears to hunt animals and other wooden tools
Made hand axes for hunting animals
Developed a pre linguistic system of communication
Became extinct 300 000 years ago
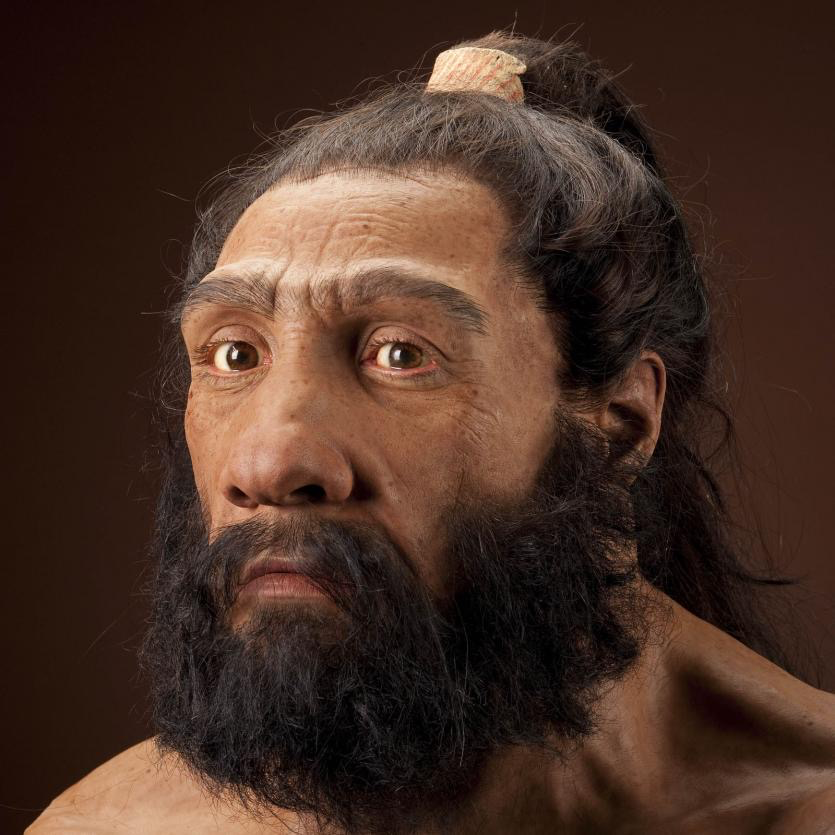

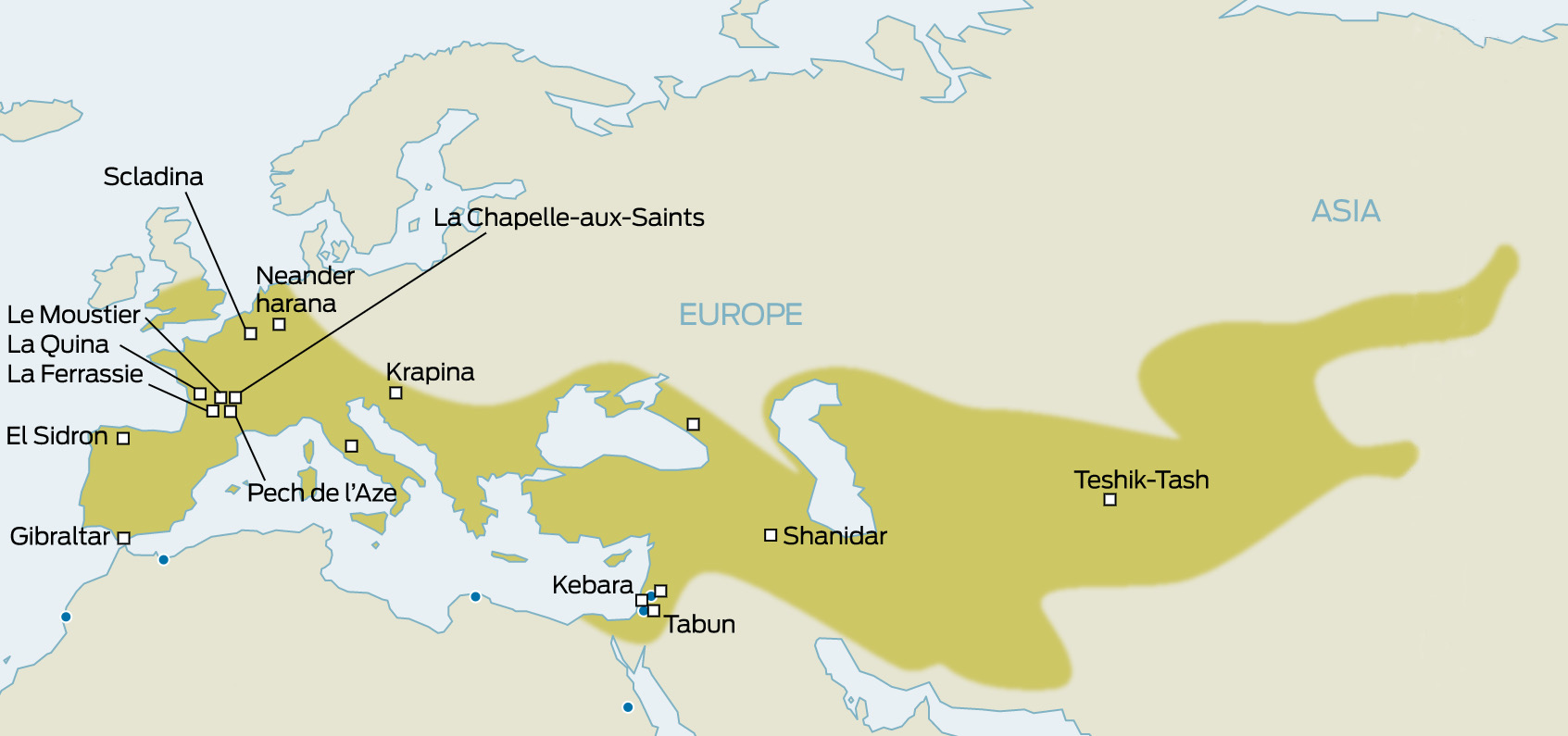
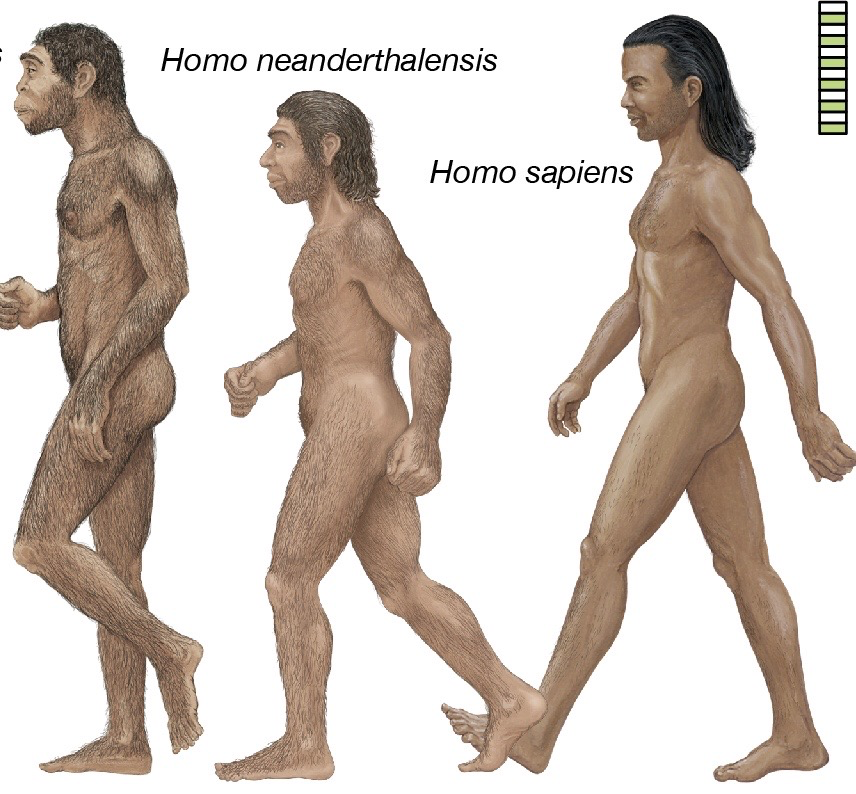
Homo Neanderthalensis
Evolved from Homo Heidelbergensis in Europe and Asia around 300 000 years ago
Used a range of stone tools including sharp tools like spears which they may have attached to wooden shafts to make spears
Used hearths for warmth and to cook food
Wore animal hides as clothing
Used caves as shelters and made open air shelters
Performed burials
Hunted large animals, ate large amounts of meat supplemented with vegetables
Became extinct between 130 00- 40 000 years ago
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
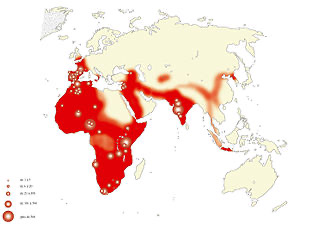
Out of Africa
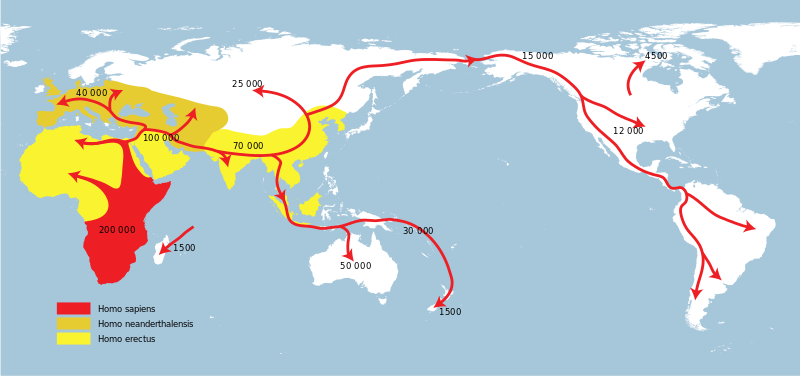
The oldest known expansions of archaic humans out of Africa happened around 2.1m years ago by homo erectus ergaster or homo erectus georgicus where remains were found in Gerogia of West Asia dating to 2.1m years ago and then branching further into Eurasia around 1.75m years ago. Their descendents Homo erectus then would have spread to South East Asia by 1.6m years ago.
Homo Erectus would have moved into Europe around 1.4m years ago.
It may have also been homo habilis who reached West Asia before evolving into Homo Erectus ans dispersing from West to East Asia, South East Asia, back to Africa and Europe.
Homo erectus may have migrated out of Africa for a number of reasons.
1. Due to changes in climate available resources would be limited and homo erectus need to find food elsewhere in order to survive.
2. Homo erectus may have followed animal migrations to the North during wetter periods in order to scavenge from them.
3. Homo erectus were successful in Eurasia because of the absence of diseases passed from animals to humans outside of their original habit.
Change in physiological traits between homo habilis and homo erectus allowed for better walking energy efficiency and endurance as well as dehydrating slower



























